NERC Compliance Experience, training, and well-developed procedures in your facility may mean that problems rarely arise. After all, in a perfect world, everything runs smoothly and goes according to plan. In the real world, though, you must plan to encounter problems and set expectations that problems will be identified, causes determined, and actions taken to correct them.
A corrective action process is a fundamental management tool vital to your continual improvement efforts and regulatory compliance. Effective resolution of issues requires a process to ensure concerns are identified, are evaluated for scope and significance, and are prioritized, and that corrective actions are implemented to prevent recurrence.
Corrective action is a process of feedback and improvement. Corrective actions are taken in response to customer NERC complaints, to unacceptable levels of non-conformance, and to issues identified through audits, investigations, assessments, and employee input.
What can a corrective action process do for you?
A proper corrective action system detects, resolves, and precludes recurring nonconformances. An in-depth understanding of how to conduct corrective action in response to non-conforming equipment or services is essential to achieve maximum reliability.
What information do you need to capture to implement corrective action?
Your corrective action program should document information on deficiencies. This can be done by capturing important information in something as simple as a table or a spread sheet, as shown below.
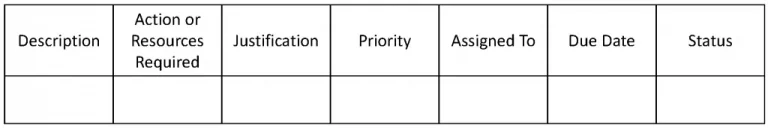
Your corrective action program should include
- a full description of the deficiency.
- assignment to the person or department best able to address the issue.
- any required resources to address the deficiency.
- cause determination.
- the action that should be taken to correct the deficiency and restore compliance.
- action(s) to preclude recurrence.
- impact and the need to correct the deficiency.
- a due date.
- regular review to track progress.
- review of effectiveness of corrective actions taken.
Report significant deficiencies to management along with appropriate information to explain the problem, how to correct it, and the reasons it needs to be addressed in order to gain management support for action. Periodically inform management of the status of corrective actions until deficiencies have been resolved.

How do you prioritize corrective actions?
Not all gaps or deficiencies are equally important. Funding and time are usually limited, so prioritizing corrective actions is helpful. Setting priorities also can identify significant deficiencies that should be reported to management and corrected as quickly as possible. Criteria or categories for corrective action may include the following:
- Regulatory compliance/conformity to national standards
- Hazards to health and safety
- Hazards to property, operations, or the environment
- Following industry best practices
The take away:
A corrective action process is a fundamental management tool vital to your continual improvement efforts and regulatory compliance. Effective resolution of issues requires a process to ensure concerns are identified, are evaluated for scope and significance, and are prioritized, and that corrective actions are developed, tracked, and implemented to prevent recurrence.

What can you do?
Develop your corrective action process with procedures to complete these key tasks:
- Assess and evaluate red flags for nonconformance (customer complaints, audit findings, process parameters, etc.)
- Identify legitimate nonconformances and related issues.
- Use risk management protocols to ensure major nonconformances are top priority (most impactful or risk significant).
- Establish clearly identified personnel roles and responsibilities, including supplier responsibilities, for defining, acting on, and closing identified issues.
- Define the problem specifically (create a problem statement).
- Capture and enter issues into the corrective action process.
- Evaluate issues for extent of condition and cause.
- Assess the enabling or contributing condition(s) and root causes.
- Define proper actions and implement solutions.
- Take actions to preclude recurrence.
- Review and verify the effectiveness of the problem resolution.
Disclaimer: Any opinions expressed in the blog do not necessarily reflect the opinions of Certrec. The content of this blog is meant for informational purposes only.












